diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index 6590ec42..c231d44b 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -108,6 +108,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0876 |[Middle of the Linked List](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0876_middle_of_the_linked_list)| Easy | Two_Pointers, Linked_List | 136 | 76.52
| 0142 |[Linked List Cycle II](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0142_linked_list_cycle_ii)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Hash_Table, Two_Pointers, Linked_List | 192 | 63.39
#### Day 5 Greedy
@@ -435,6 +436,7 @@
| 0328 |[Odd Even Linked List](src/main/kotlin/g0301_0400/s0328_odd_even_linked_list)| Medium | Top_Interview_Questions, Linked_List | 216 | 86.96
| 0061 |[Rotate List](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0061_rotate_list)| Medium | Two_Pointers, Linked_List | 193 | 92.16
| 0024 |[Swap Nodes in Pairs](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0024_swap_nodes_in_pairs)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Linked_List, Recursion | 149 | 99.39
+| 0876 |[Middle of the Linked List](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0876_middle_of_the_linked_list)| Easy | Two_Pointers, Linked_List | 136 | 76.52
| 0142 |[Linked List Cycle II](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0142_linked_list_cycle_ii)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Hash_Table, Two_Pointers, Linked_List | 192 | 63.39
| 0141 |[Linked List Cycle](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0141_linked_list_cycle)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Hash_Table, Two_Pointers, Linked_List | 223 | 91.85
| 0206 |[Reverse Linked List](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0206_reverse_linked_list)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Linked_List, Recursion | 279 | 45.78
@@ -824,6 +826,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0876 |[Middle of the Linked List](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0876_middle_of_the_linked_list)| Easy | Two_Pointers, Linked_List | 136 | 76.52
| 0019 |[Remove Nth Node From End of List](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0019_remove_nth_node_from_end_of_list)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Two_Pointers, Linked_List | 180 | 91.58
#### Day 6 Sliding Window
@@ -1146,6 +1149,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0875 |[Koko Eating Bananas](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0875_koko_eating_bananas)| Medium | Array, Binary_Search | 267 | 93.85
#### Day 5
@@ -1444,6 +1448,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0876 |[Middle of the Linked List](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0876_middle_of_the_linked_list)| Easy | Two_Pointers, Linked_List | 136 | 76.52
| 0104 |[Maximum Depth of Binary Tree](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0104_maximum_depth_of_binary_tree)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree | 236 | 83.39
| 0404 |[Sum of Left Leaves](src/main/kotlin/g0401_0500/s0404_sum_of_left_leaves)| Easy | Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree | 173 | 86.05
@@ -1679,6 +1684,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0886 |[Possible Bipartition](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0886_possible_bipartition)| Medium | Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Graph, Union_Find | 397 | 100.00
| 0785 |[Is Graph Bipartite?](src/main/kotlin/g0701_0800/s0785_is_graph_bipartite)| Medium | Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Graph, Union_Find | 215 | 82.35
## Algorithms
@@ -1687,6 +1693,27 @@
|------|----------------|-------------|-------------|----------|--------
| 1143 |[Longest Common Subsequence](src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1143_longest_common_subsequence)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, String, Dynamic_Programming, Algorithm_II_Day_17_Dynamic_Programming, Dynamic_Programming_I_Day_19, Udemy_Dynamic_Programming | 307 | 38.36
| 0994 |[Rotting Oranges](src/main/kotlin/g0901_1000/s0994_rotting_oranges)| Medium | Array, Breadth_First_Search, Matrix, Algorithm_I_Day_9_Breadth_First_Search_Depth_First_Search, Level_2_Day_10_Graph/BFS/DFS | 308 | 57.93
+| 0891 |[Sum of Subsequence Widths](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0891_sum_of_subsequence_widths)| Hard | Array, Math, Sorting | 481 | 100.00
+| 0890 |[Find and Replace Pattern](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0890_find_and_replace_pattern)| Medium | Array, String, Hash_Table | 150 | 100.00
+| 0889 |[Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Postorder Traversal](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0889_construct_binary_tree_from_preorder_and_postorder_traversal)| Medium | Array, Hash_Table, Tree, Binary_Tree, Divide_and_Conquer | 168 | 100.00
+| 0888 |[Fair Candy Swap](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0888_fair_candy_swap)| Easy | Array, Hash_Table, Sorting, Binary_Search | 318 | 100.00
+| 0887 |[Super Egg Drop](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0887_super_egg_drop)| Hard | Dynamic_Programming, Math, Binary_Search | 119 | 100.00
+| 0886 |[Possible Bipartition](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0886_possible_bipartition)| Medium | Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Graph, Union_Find, Graph_Theory_I_Day_14_Graph_Theory | 397 | 100.00
+| 0885 |[Spiral Matrix III](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0885_spiral_matrix_iii)| Medium | Array, Matrix, Simulation | 265 | 100.00
+| 0884 |[Uncommon Words from Two Sentences](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0884_uncommon_words_from_two_sentences)| Easy | String, Hash_Table | 171 | 100.00
+| 0883 |[Projection Area of 3D Shapes](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0883_projection_area_of_3d_shapes)| Easy | Array, Math, Matrix, Geometry | 173 | 100.00
+| 0882 |[Reachable Nodes In Subdivided Graph](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0882_reachable_nodes_in_subdivided_graph)| Hard | Heap_Priority_Queue, Graph, Shortest_Path | 434 | 100.00
+| 0881 |[Boats to Save People](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0881_boats_to_save_people)| Medium | Array, Sorting, Greedy, Two_Pointers | 370 | 96.07
+| 0880 |[Decoded String at Index](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0880_decoded_string_at_index)| Medium | String, Stack | 134 | 100.00
+| 0879 |[Profitable Schemes](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0879_profitable_schemes)| Hard | Array, Dynamic_Programming | 198 | 75.00
+| 0878 |[Nth Magical Number](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0878_nth_magical_number)| Hard | Math, Binary_Search | 124 | 100.00
+| 0877 |[Stone Game](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0877_stone_game)| Medium | Array, Dynamic_Programming, Math, Game_Theory | 136 | 88.24
+| 0876 |[Middle of the Linked List](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0876_middle_of_the_linked_list)| Easy | Two_Pointers, Linked_List, Algorithm_I_Day_5_Two_Pointers, Programming_Skills_I_Day_10_Linked_List_and_Tree, Level_1_Day_4_Linked_List, Udemy_Linked_List | 136 | 76.52
+| 0875 |[Koko Eating Bananas](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0875_koko_eating_bananas)| Medium | Array, Binary_Search, Binary_Search_II_Day_4 | 267 | 93.85
+| 0874 |[Walking Robot Simulation](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0874_walking_robot_simulation)| Medium | Array, Simulation | 274 | 100.00
+| 0873 |[Length of Longest Fibonacci Subsequence](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0873_length_of_longest_fibonacci_subsequence)| Medium | Array, Hash_Table, Dynamic_Programming | 341 | 90.00
+| 0872 |[Leaf-Similar Trees](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0872_leaf_similar_trees)| Easy | Depth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree | 140 | 100.00
+| 0871 |[Minimum Number of Refueling Stops](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0871_minimum_number_of_refueling_stops)| Hard | Array, Dynamic_Programming, Greedy, Heap_Priority_Queue | 203 | 92.86
| 0870 |[Advantage Shuffle](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0870_advantage_shuffle)| Medium | Array, Sorting, Greedy | 698 | 100.00
| 0869 |[Reordered Power of 2](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0869_reordered_power_of_2)| Medium | Math, Sorting, Counting, Enumeration | 145 | 87.50
| 0868 |[Binary Gap](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0868_binary_gap)| Easy | Bit_Manipulation | 142 | 100.00
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0814_binary_tree_pruning/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0814_binary_tree_pruning/readme.md
index b1aac0a2..0ba97580 100644
--- a/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0814_binary_tree_pruning/readme.md
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0814_binary_tree_pruning/readme.md
@@ -49,7 +49,7 @@ The diagram on the right represents the answer.
```kotlin
import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode
-/**
+/*
* Example:
* var ti = TreeNode(5)
* var v = ti.`val`
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0817_linked_list_components/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0817_linked_list_components/readme.md
index 5778754e..c88ab2f8 100644
--- a/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0817_linked_list_components/readme.md
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0817_linked_list_components/readme.md
@@ -44,7 +44,7 @@ Return _the number of connected components in_ `nums` _where two values are conn
```kotlin
import com_github_leetcode.ListNode
-/**
+/*
* Example:
* var li = ListNode(5)
* var v = li.`val`
@@ -53,7 +53,6 @@ import com_github_leetcode.ListNode
* var next: ListNode? = null
* }
*/
-
@Suppress("NAME_SHADOWING")
class Solution {
fun numComponents(head: ListNode?, nums: IntArray): Int {
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0871_minimum_number_of_refueling_stops/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0871_minimum_number_of_refueling_stops/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ab99aff1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0871_minimum_number_of_refueling_stops/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,90 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 871\. Minimum Number of Refueling Stops
+
+Hard
+
+A car travels from a starting position to a destination which is `target` miles east of the starting position.
+
+There are gas stations along the way. The gas stations are represented as an array `stations` where stations[i] = [positioni, fueli] indicates that the ith gas station is positioni miles east of the starting position and has fueli liters of gas.
+
+The car starts with an infinite tank of gas, which initially has `startFuel` liters of fuel in it. It uses one liter of gas per one mile that it drives. When the car reaches a gas station, it may stop and refuel, transferring all the gas from the station into the car.
+
+Return _the minimum number of refueling stops the car must make in order to reach its destination_. If it cannot reach the destination, return `-1`.
+
+Note that if the car reaches a gas station with `0` fuel left, the car can still refuel there. If the car reaches the destination with `0` fuel left, it is still considered to have arrived.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** target = 1, startFuel = 1, stations = []
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:** We can reach the target without refueling.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** target = 100, startFuel = 1, stations = \[\[10,100]]
+
+**Output:** -1
+
+**Explanation:** We can not reach the target (or even the first gas station).
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** target = 100, startFuel = 10, stations = \[\[10,60],[20,30],[30,30],[60,40]]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** We start with 10 liters of fuel. We drive to position 10, expending 10 liters of fuel.
+
+We refuel from 0 liters to 60 liters of gas.
+
+Then, we drive from position 10 to position 60 (expending 50 liters of fuel),
+
+and refuel from 10 liters to 50 liters of gas. We then drive to and reach the target.
+
+We made 2 refueling stops along the way, so we return 2.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= target, startFuel <= 109
+* `0 <= stations.length <= 500`
+* 0 <= positioni <= positioni+1 < target
+* 1 <= fueli < 109
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.PriorityQueue
+
+class Solution {
+ fun minRefuelStops(target: Int, startFuel: Int, stations: Array?): Int {
+ if (startFuel >= target) {
+ return 0
+ } else if (stations.isNullOrEmpty()) {
+ return -1
+ }
+ val pq = PriorityQueue { a: IntArray, b: IntArray ->
+ b[1] - a[1]
+ }
+ var start = 0
+ val end = stations.size
+ var currentFuel = startFuel
+ var stops = 0
+ while (currentFuel < target) {
+ while (start < end && currentFuel >= stations[start][0]) {
+ pq.add(stations[start++])
+ }
+ if (pq.isEmpty()) {
+ return -1
+ }
+ val current = pq.poll()
+ currentFuel += current[1]
+ stops++
+ }
+ return stops
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0872_leaf_similar_trees/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0872_leaf_similar_trees/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7bbbb2b8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0872_leaf_similar_trees/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 872\. Leaf-Similar Trees
+
+Easy
+
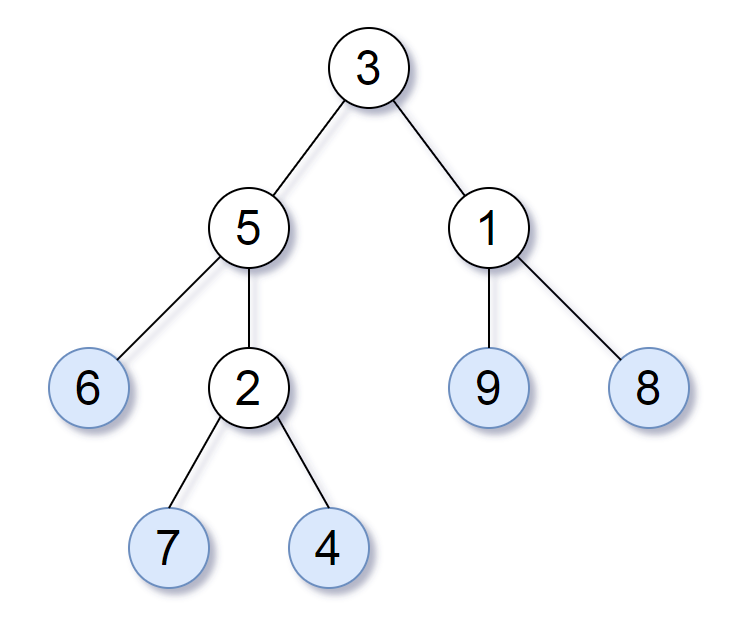
+Consider all the leaves of a binary tree, from left to right order, the values of those leaves form a **leaf value sequence**_._
+
+
+
+For example, in the given tree above, the leaf value sequence is `(6, 7, 4, 9, 8)`.
+
+Two binary trees are considered _leaf-similar_ if their leaf value sequence is the same.
+
+Return `true` if and only if the two given trees with head nodes `root1` and `root2` are leaf-similar.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
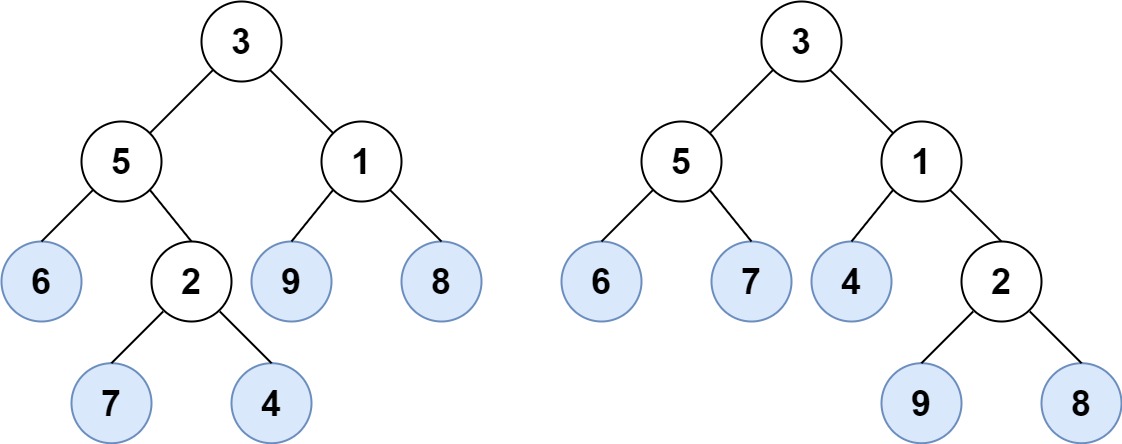
+**Input:** root1 = [3,5,1,6,2,9,8,null,null,7,4], root2 = [3,5,1,6,7,4,2,null,null,null,null,null,null,9,8]
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
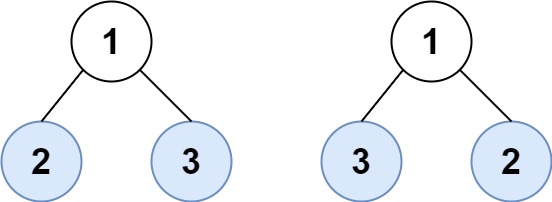
+**Input:** root1 = [1,2,3], root2 = [1,3,2]
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of nodes in each tree will be in the range `[1, 200]`.
+* Both of the given trees will have values in the range `[0, 200]`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode
+
+/*
+ * Example:
+ * var ti = TreeNode(5)
+ * var v = ti.`val`
+ * Definition for a binary tree node.
+ * class TreeNode(var `val`: Int) {
+ * var left: TreeNode? = null
+ * var right: TreeNode? = null
+ * }
+ */
+class Solution {
+ fun leafSimilar(root1: TreeNode?, root2: TreeNode?): Boolean {
+ val list1: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ val list2: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ preOrder(root1, list1)
+ preOrder(root2, list2)
+ // compare the lists
+ if (list1.size != list2.size) {
+ return false
+ }
+ for (i in list1.indices) {
+ if (list1[i] != list2[i]) {
+ return false
+ }
+ }
+ return true
+ }
+
+ private fun preOrder(root: TreeNode?, list: MutableList) {
+ if (root != null) {
+ if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
+ list.add(root.`val`)
+ }
+ preOrder(root.left, list)
+ preOrder(root.right, list)
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0873_length_of_longest_fibonacci_subsequence/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0873_length_of_longest_fibonacci_subsequence/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a840c9cb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0873_length_of_longest_fibonacci_subsequence/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 873\. Length of Longest Fibonacci Subsequence
+
+Medium
+
+A sequence x1, x2, ..., xn is _Fibonacci-like_ if:
+
+* `n >= 3`
+* xi + xi+1 == xi+2 for all `i + 2 <= n`
+
+Given a **strictly increasing** array `arr` of positive integers forming a sequence, return _the **length** of the longest Fibonacci-like subsequence of_ `arr`. If one does not exist, return `0`.
+
+A **subsequence** is derived from another sequence `arr` by deleting any number of elements (including none) from `arr`, without changing the order of the remaining elements. For example, `[3, 5, 8]` is a subsequence of `[3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:** The longest subsequence that is fibonacci-like: [1,2,3,5,8].
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [1,3,7,11,12,14,18]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**: The longest subsequence that is fibonacci-like: [1,11,12], [3,11,14] or [7,11,18].
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `3 <= arr.length <= 1000`
+* 1 <= arr[i] < arr[i + 1] <= 109
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun lenLongestFibSubseq(arr: IntArray?): Int {
+ if (arr == null || arr.size < 3) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ val len = arr.size
+ val dp = Array(len) { IntArray(len) }
+ var ans = 0
+ for (i in 2 until len) {
+ var left = 0
+ var right = i - 1
+ while (left < right) {
+ if (arr[left] + arr[right] < arr[i]) {
+ left++
+ } else if (arr[left] + arr[right] > arr[i]) {
+ right--
+ } else {
+ // dp[right][i] = Math.max(dp[right][i], dp[left][right] + 1);
+ dp[right][i] = dp[left][right] + 1
+ ans = Math.max(ans, dp[right][i])
+ left++
+ right--
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return if (ans > 0) ans + 2 else 0
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0874_walking_robot_simulation/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0874_walking_robot_simulation/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8f3e5b64
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0874_walking_robot_simulation/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,186 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 874\. Walking Robot Simulation
+
+Medium
+
+A robot on an infinite XY-plane starts at point `(0, 0)` facing north. The robot can receive a sequence of these three possible types of `commands`:
+
+* `-2`: Turn left `90` degrees.
+* `-1`: Turn right `90` degrees.
+* `1 <= k <= 9`: Move forward `k` units, one unit at a time.
+
+Some of the grid squares are `obstacles`. The ith obstacle is at grid point obstacles[i] = (xi, yi). If the robot runs into an obstacle, then it will instead stay in its current location and move on to the next command.
+
+Return _the **maximum Euclidean distance** that the robot ever gets from the origin **squared** (i.e. if the distance is_ `5`_, return_ `25`_)_.
+
+**Note:**
+
+* North means +Y direction.
+* East means +X direction.
+* South means -Y direction.
+* West means -X direction.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** commands = [4,-1,3], obstacles = []
+
+**Output:** 25
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The robot starts at (0, 0):
+
+1. Move north 4 units to (0, 4).
+
+2. Turn right.
+
+3. Move east 3 units to (3, 4).
+
+The furthest point the robot ever gets from the origin is (3, 4), which squared is 32 + 42 = 25 units away.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** commands = [4,-1,4,-2,4], obstacles = \[\[2,4]]
+
+**Output:** 65
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The robot starts at (0, 0):
+
+1. Move north 4 units to (0, 4).
+
+2. Turn right.
+
+3. Move east 1 unit and get blocked by the obstacle at (2, 4), robot is at (1, 4).
+
+4. Turn left.
+
+5. Move north 4 units to (1, 8).
+
+The furthest point the robot ever gets from the origin is (1, 8), which squared is 12 + 82 = 65 units away.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** commands = [6,-1,-1,6], obstacles = []
+
+**Output:** 36
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The robot starts at (0, 0):
+
+1. Move north 6 units to (0, 6).
+
+2. Turn right.
+
+3. Turn right.
+
+4. Move south 6 units to (0, 0).
+
+The furthest point the robot ever gets from the origin is (0, 6), which squared is 62 = 36 units away.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= commands.length <= 104
+* `commands[i]` is either `-2`, `-1`, or an integer in the range `[1, 9]`.
+* 0 <= obstacles.length <= 104
+* -3 * 104 <= xi, yi <= 3 * 104
+* The answer is guaranteed to be less than 231.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ internal class Point(var row: Int, var column: Int) {
+ override fun equals(other: Any?): Boolean {
+ if (other !is Point) {
+ return false
+ }
+ return other.row == row && other.column == column
+ }
+
+ override fun hashCode(): Int {
+ return row * column * 31
+ }
+ }
+
+ internal enum class Direction(val x: Int, val y: Int) {
+ NORTH(0, 1) {
+ override fun turnLeft(): Direction {
+ return WEST
+ }
+
+ override fun turnRight(): Direction {
+ return EAST
+ }
+ },
+ EAST(1, 0) {
+ override fun turnLeft(): Direction {
+ return NORTH
+ }
+
+ override fun turnRight(): Direction {
+ return SOUTH
+ }
+ },
+ SOUTH(0, -1) {
+ override fun turnLeft(): Direction {
+ return EAST
+ }
+
+ override fun turnRight(): Direction {
+ return WEST
+ }
+ },
+ WEST(-1, 0) {
+ override fun turnLeft(): Direction {
+ return SOUTH
+ }
+
+ override fun turnRight(): Direction {
+ return NORTH
+ }
+ };
+
+ abstract fun turnLeft(): Direction
+ abstract fun turnRight(): Direction
+ fun next(p: Point): Point {
+ return Point(p.row + x, p.column + y)
+ }
+ }
+
+ fun robotSim(commands: IntArray, obstacles: Array): Int {
+ val set: MutableSet = HashSet()
+ for (i in obstacles.indices) {
+ val p = Point(obstacles[i][0], obstacles[i][1])
+ set.add(p)
+ }
+ var direction = Direction.NORTH
+ var p = Point(0, 0)
+ var maxDistance = 0
+ for (i in commands.indices) {
+ val command = commands[i]
+ if (command == -1) {
+ direction = direction.turnRight()
+ continue
+ }
+ if (command == -2) {
+ direction = direction.turnLeft()
+ continue
+ }
+ for (j in 0 until command) {
+ val destination = direction.next(p)
+ if (set.contains(destination)) {
+ break
+ }
+ p = destination
+ }
+ maxDistance = maxDistance.coerceAtLeast(p.row * p.row + p.column * p.column)
+ }
+ return maxDistance
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0875_koko_eating_bananas/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0875_koko_eating_bananas/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..12a5d635
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0875_koko_eating_bananas/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 875\. Koko Eating Bananas
+
+Medium
+
+Koko loves to eat bananas. There are `n` piles of bananas, the ith pile has `piles[i]` bananas. The guards have gone and will come back in `h` hours.
+
+Koko can decide her bananas-per-hour eating speed of `k`. Each hour, she chooses some pile of bananas and eats `k` bananas from that pile. If the pile has less than `k` bananas, she eats all of them instead and will not eat any more bananas during this hour.
+
+Koko likes to eat slowly but still wants to finish eating all the bananas before the guards return.
+
+Return _the minimum integer_ `k` _such that she can eat all the bananas within_ `h` _hours_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** piles = [3,6,7,11], h = 8
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** piles = [30,11,23,4,20], h = 5
+
+**Output:** 30
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** piles = [30,11,23,4,20], h = 6
+
+**Output:** 23
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= piles.length <= 104
+* piles.length <= h <= 109
+* 1 <= piles[i] <= 109
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun minEatingSpeed(piles: IntArray, h: Int): Int {
+ var maxP = piles[0]
+ var sumP = 0L
+ for (pile in piles) {
+ maxP = maxP.coerceAtLeast(pile)
+ sumP += pile.toLong()
+ }
+ // binary search
+ var low = ((sumP - 1) / h + 1).toInt()
+ var high = maxP
+ while (low < high) {
+ val mid = low + (high - low) / 2
+ if (isPossible(piles, mid, h)) {
+ high = mid
+ } else {
+ low = mid + 1
+ }
+ }
+ return low
+ }
+
+ private fun isPossible(piles: IntArray, k: Int, h: Int): Boolean {
+ var sum = 0
+ for (pile in piles) {
+ sum += (pile - 1) / k + 1
+ }
+ return sum <= h
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0876_middle_of_the_linked_list/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0876_middle_of_the_linked_list/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..39221089
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0876_middle_of_the_linked_list/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 876\. Middle of the Linked List
+
+Easy
+
+Given the `head` of a singly linked list, return _the middle node of the linked list_.
+
+If there are two middle nodes, return **the second middle** node.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** head = [1,2,3,4,5]
+
+**Output:** [3,4,5]
+
+**Explanation:** The middle node of the list is node 3.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** head = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
+
+**Output:** [4,5,6]
+
+**Explanation:** Since the list has two middle nodes with values 3 and 4, we return the second one.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of nodes in the list is in the range `[1, 100]`.
+* `1 <= Node.val <= 100`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.ListNode
+
+/*
+ * Example:
+ * var li = ListNode(5)
+ * var v = li.`val`
+ * Definition for singly-linked list.
+ * class ListNode(var `val`: Int) {
+ * var next: ListNode? = null
+ * }
+ */
+class Solution {
+ fun middleNode(head: ListNode?): ListNode? {
+ var fast = head
+ var slow = head
+ while (fast?.next != null) {
+ fast = fast.next!!.next
+ slow = slow!!.next
+ }
+ return slow
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0877_stone_game/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0877_stone_game/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f8d2e7ea
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0877_stone_game/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 877\. Stone Game
+
+Medium
+
+Alice and Bob play a game with piles of stones. There are an **even** number of piles arranged in a row, and each pile has a **positive** integer number of stones `piles[i]`.
+
+The objective of the game is to end with the most stones. The **total** number of stones across all the piles is **odd**, so there are no ties.
+
+Alice and Bob take turns, with **Alice starting first**. Each turn, a player takes the entire pile of stones either from the **beginning** or from the **end** of the row. This continues until there are no more piles left, at which point the person with the **most stones wins**.
+
+Assuming Alice and Bob play optimally, return `true` _if Alice wins the game, or_ `false` _if Bob wins_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** piles = [5,3,4,5]
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Alice starts first, and can only take the first 5 or the last 5.
+
+Say she takes the first 5, so that the row becomes [3, 4, 5].
+
+If Bob takes 3, then the board is [4, 5], and Alice takes 5 to win with 10 points.
+
+If Bob takes the last 5, then the board is [3, 4], and Alice takes 4 to win with 9 points.
+
+This demonstrated that taking the first 5 was a winning move for Alice, so we return true.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** piles = [3,7,2,3]
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `2 <= piles.length <= 500`
+* `piles.length` is **even**.
+* `1 <= piles[i] <= 500`
+* `sum(piles[i])` is **odd**.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun stoneGame(piles: IntArray): Boolean {
+ var low = 0
+ var high = piles.size - 1
+ var alice = 0
+ var bob = 0
+ while (low < high) {
+ alice += piles[low].coerceAtLeast(piles[high])
+ bob += piles[low].coerceAtMost(piles[high])
+ low++
+ high--
+ }
+ return alice > bob
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0878_nth_magical_number/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0878_nth_magical_number/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e5d2b8a9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0878_nth_magical_number/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 878\. Nth Magical Number
+
+Hard
+
+A positive integer is _magical_ if it is divisible by either `a` or `b`.
+
+Given the three integers `n`, `a`, and `b`, return the nth magical number. Since the answer may be very large, **return it modulo** 109 + 7.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 1, a = 2, b = 3
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 4, a = 2, b = 3
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= n <= 109
+* 2 <= a, b <= 4 * 104
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+@Suppress("NAME_SHADOWING")
+class Solution {
+ fun nthMagicalNumber(n: Int, a: Int, b: Int): Int {
+ val c = lcm(a.toLong(), b.toLong())
+ var l: Long = 2
+ var r = n * c
+ var ans = r
+ while (l <= r) {
+ val mid = l + (r - l) / 2
+ val cnt = mid / a + mid / b - mid / c
+ if (cnt < n) {
+ l = mid + 1
+ } else {
+ ans = mid
+ r = mid - 1
+ }
+ }
+ return (ans % MOD).toInt()
+ }
+
+ private fun lcm(a: Long, b: Long): Long {
+ return a * b / gcd(a, b)
+ }
+
+ private fun gcd(a: Long, b: Long): Long {
+ var a = a
+ var b = b
+ var t: Long
+ while (b != 0L) {
+ t = b
+ b = a % b
+ a = t
+ }
+ return a
+ }
+
+ companion object {
+ private const val MOD = 1000000007
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0879_profitable_schemes/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0879_profitable_schemes/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..548dbe14
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0879_profitable_schemes/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 879\. Profitable Schemes
+
+Hard
+
+There is a group of `n` members, and a list of various crimes they could commit. The ith crime generates a `profit[i]` and requires `group[i]` members to participate in it. If a member participates in one crime, that member can't participate in another crime.
+
+Let's call a **profitable scheme** any subset of these crimes that generates at least `minProfit` profit, and the total number of members participating in that subset of crimes is at most `n`.
+
+Return the number of schemes that can be chosen. Since the answer may be very large, **return it modulo** 109 + 7.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 5, minProfit = 3, group = [2,2], profit = [2,3]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** To make a profit of at least 3, the group could either commit crimes 0 and 1, or just crime 1. In total, there are 2 schemes.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 10, minProfit = 5, group = [2,3,5], profit = [6,7,8]
+
+**Output:** 7
+
+**Explanation:** To make a profit of at least 5, the group could commit any crimes, as long as they commit one. There are 7 possible schemes: (0), (1), (2), (0,1), (0,2), (1,2), and (0,1,2).
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= n <= 100`
+* `0 <= minProfit <= 100`
+* `1 <= group.length <= 100`
+* `1 <= group[i] <= 100`
+* `profit.length == group.length`
+* `0 <= profit[i] <= 100`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun profitableSchemes(n: Int, minProfit: Int, group: IntArray, profit: IntArray): Int {
+ val dp = Array(n + 1) { LongArray(minProfit + 1) }
+ val modulus = 1000000007L
+ for (i in dp.indices) {
+ dp[i][0] = 1
+ }
+ for (i in group.indices) {
+ val currWorker = group[i]
+ val currProfit = profit[i]
+ for (j in dp.size - 1 downTo currWorker) {
+ for (k in dp[j].indices.reversed()) {
+ dp[j][k] = (
+ (dp[j][k] + dp[j - currWorker][(k - currProfit).coerceAtLeast(0)]) %
+ modulus
+ )
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[n][minProfit].toInt()
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0880_decoded_string_at_index/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0880_decoded_string_at_index/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..569c6ab7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0880_decoded_string_at_index/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 880\. Decoded String at Index
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an encoded string `s`. To decode the string to a tape, the encoded string is read one character at a time and the following steps are taken:
+
+* If the character read is a letter, that letter is written onto the tape.
+* If the character read is a digit `d`, the entire current tape is repeatedly written `d - 1` more times in total.
+
+Given an integer `k`, return _the_ kth _letter (**1-indexed)** in the decoded string_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "leet2code3", k = 10
+
+**Output:** "o"
+
+**Explanation:** The decoded string is "leetleetcodeleetleetcodeleetleetcode". The 10th letter in the string is "o".
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "ha22", k = 5
+
+**Output:** "h"
+
+**Explanation:** The decoded string is "hahahaha". The 5th letter is "h".
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "a2345678999999999999999", k = 1
+
+**Output:** "a"
+
+**Explanation:** The decoded string is "a" repeated 8301530446056247680 times. The 1st letter is "a".
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `2 <= s.length <= 100`
+* `s` consists of lowercase English letters and digits `2` through `9`.
+* `s` starts with a letter.
+* 1 <= k <= 109
+* It is guaranteed that `k` is less than or equal to the length of the decoded string.
+* The decoded string is guaranteed to have less than 263 letters.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+@Suppress("NAME_SHADOWING")
+class Solution {
+ fun decodeAtIndex(s: String, k: Int): String {
+ var k = k
+ var i = 0
+ var count: Long = 0
+ while (i < s.length && count <= k) {
+ val c = s[i]
+ count = if (Character.isDigit(c)) count * (c.code - '0'.code) else count + 1
+ i++
+ }
+ i--
+ while (i < s.length) {
+ val c = s[i]
+ if (Character.isDigit(c)) {
+ count /= (c.code - '0'.code).toLong()
+ k %= count.toInt()
+ } else {
+ if (k % count == 0L) {
+ break
+ }
+ --count
+ }
+ i--
+ }
+ return s[i].toString()
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0881_boats_to_save_people/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0881_boats_to_save_people/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2ab0f7b2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0881_boats_to_save_people/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 881\. Boats to Save People
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an array `people` where `people[i]` is the weight of the ith person, and an **infinite number of boats** where each boat can carry a maximum weight of `limit`. Each boat carries at most two people at the same time, provided the sum of the weight of those people is at most `limit`.
+
+Return _the minimum number of boats to carry every given person_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** people = [1,2], limit = 3
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:** 1 boat (1, 2)
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** people = [3,2,2,1], limit = 3
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** 3 boats (1, 2), (2) and (3)
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** people = [3,5,3,4], limit = 5
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:** 4 boats (3), (3), (4), (5)
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= people.length <= 5 * 104
+* 1 <= people[i] <= limit <= 3 * 104
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun numRescueBoats(people: IntArray, limit: Int): Int {
+ people.sort()
+ var i = 0
+ var j = people.size - 1
+ var boats = 0
+ while (i < j) {
+ if (people[i] + people[j] <= limit) {
+ boats++
+ i++
+ j--
+ } else if (people[i] + people[j] > limit) {
+ boats++
+ j--
+ }
+ }
+ return if (i == j) {
+ boats + 1
+ } else boats
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0882_reachable_nodes_in_subdivided_graph/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0882_reachable_nodes_in_subdivided_graph/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c25e15f3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0882_reachable_nodes_in_subdivided_graph/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 882\. Reachable Nodes In Subdivided Graph
+
+Hard
+
+You are given an undirected graph (the **"original graph"**) with `n` nodes labeled from `0` to `n - 1`. You decide to **subdivide** each edge in the graph into a chain of nodes, with the number of new nodes varying between each edge.
+
+The graph is given as a 2D array of `edges` where edges[i] = [ui, vi, cnti] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ui and vi in the original graph, and cnti is the total number of new nodes that you will **subdivide** the edge into. Note that cnti == 0 means you will not subdivide the edge.
+
+To **subdivide** the edge [ui, vi], replace it with (cnti + 1) new edges and cnti new nodes. The new nodes are x1, x2, ..., xcnti, and the new edges are [ui, x1], [x1, x2], [x2, x3], ..., [xcnti-1, xcnti], [xcnti, vi].
+
+In this **new graph**, you want to know how many nodes are **reachable** from the node `0`, where a node is **reachable** if the distance is `maxMoves` or less.
+
+Given the original graph and `maxMoves`, return _the number of nodes that are **reachable** from node_ `0` _in the new graph_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** edges = \[\[0,1,10],[0,2,1],[1,2,2]], maxMoves = 6, n = 3
+
+**Output:** 13
+
+**Explanation:** The edge subdivisions are shown in the image above. The nodes that are reachable are highlighted in yellow.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** edges = \[\[0,1,4],[1,2,6],[0,2,8],[1,3,1]], maxMoves = 10, n = 4
+
+**Output:** 23
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** edges = \[\[1,2,4],[1,4,5],[1,3,1],[2,3,4],[3,4,5]], maxMoves = 17, n = 5
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:** Node 0 is disconnected from the rest of the graph, so only node 0 is reachable.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 0 <= edges.length <= min(n * (n - 1) / 2, 104)
+* `edges[i].length == 3`
+* 0 <= ui < vi < n
+* There are **no multiple edges** in the graph.
+* 0 <= cnti <= 104
+* 0 <= maxMoves <= 109
+* `1 <= n <= 3000`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.PriorityQueue
+
+class Solution {
+ fun reachableNodes(edges: Array, maxMoves: Int, n: Int): Int {
+ val adList = getAdList(edges, n)
+ val pQueue = PriorityQueue { a: IntArray, b: IntArray ->
+ a[1] - b[1]
+ }
+ val minDis = IntArray(n)
+ var res = 0
+ pQueue.add(intArrayOf(0, 0))
+ while (pQueue.size > 0) {
+ val poll = pQueue.poll()
+ val node = poll[0]
+ val dist = poll[1]
+ if (minDis[node] > 0) continue
+ res++
+ minDis[node] = dist
+ for (child in adList[node]!!) {
+ val cNode = child!![0]
+ val weight = child[1]
+ if (cNode != 0 && minDis[cNode] == 0) {
+ res += (maxMoves - dist).coerceAtMost(weight)
+ val cNodeDist = dist + weight + 1
+ if (cNodeDist <= maxMoves) pQueue.add(intArrayOf(cNode, cNodeDist))
+ } else {
+ res += (weight - (maxMoves - minDis[cNode]).coerceAtMost(weight)).coerceAtMost(
+ (maxMoves - dist).coerceAtMost(weight)
+ )
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return res
+ }
+
+ private fun getAdList(edges: Array, n: Int): Array?> {
+ val adList: Array?> = arrayOfNulls?>(n)
+ adList[0] = ArrayList()
+ for (edge in edges) {
+ val s = edge[0]
+ val d = edge[1]
+ val w = edge[2]
+ if (adList[s] == null) adList[s] = ArrayList()
+ if (adList[d] == null) adList[d] = ArrayList()
+ adList[s]?.add(intArrayOf(d, w))
+ adList[d]?.add(intArrayOf(s, w))
+ }
+ return adList
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0883_projection_area_of_3d_shapes/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0883_projection_area_of_3d_shapes/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0f658617
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0883_projection_area_of_3d_shapes/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 883\. Projection Area of 3D Shapes
+
+Easy
+
+You are given an `n x n` `grid` where we place some `1 x 1 x 1` cubes that are axis-aligned with the `x`, `y`, and `z` axes.
+
+Each value `v = grid[i][j]` represents a tower of `v` cubes placed on top of the cell `(i, j)`.
+
+We view the projection of these cubes onto the `xy`, `yz`, and `zx` planes.
+
+A **projection** is like a shadow, that maps our **3-dimensional** figure to a **2-dimensional** plane. We are viewing the "shadow" when looking at the cubes from the top, the front, and the side.
+
+Return _the total area of all three projections_.
+
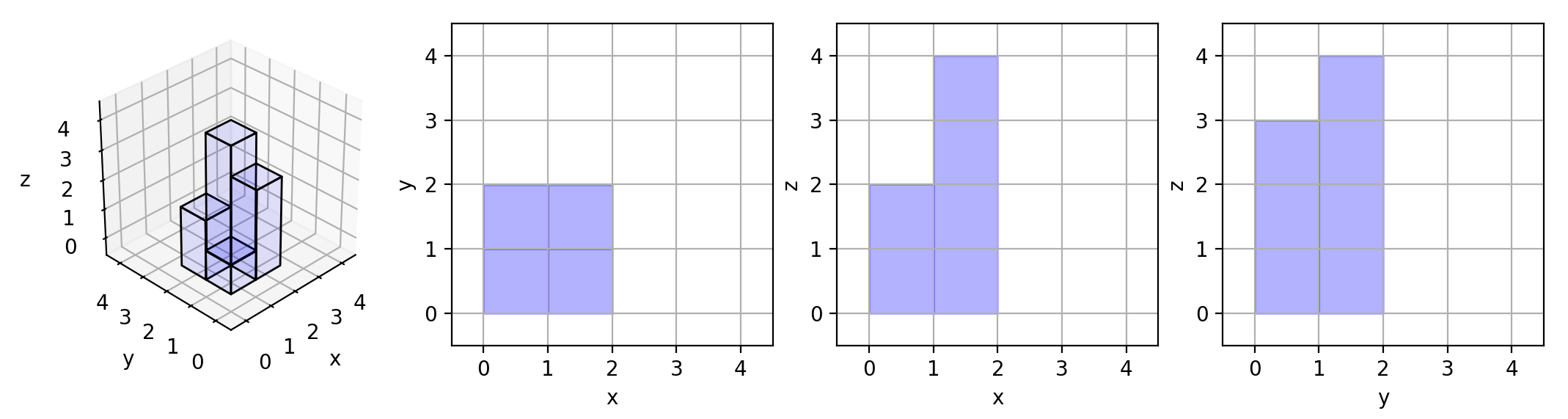
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[1,2],[3,4]]
+
+**Output:** 17
+
+**Explanation:** Here are the three projections ("shadows") of the shape made with each axis-aligned plane.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[2]]
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[1,0],[0,2]]
+
+**Output:** 8
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `n == grid.length == grid[i].length`
+* `1 <= n <= 50`
+* `0 <= grid[i][j] <= 50`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun projectionArea(grid: Array): Int {
+ val n = grid.size
+ val m = grid[0].size
+ var sum = n * m
+ var count = 0
+ for (ints in grid) {
+ var max = Int.MIN_VALUE
+ for (j in 0 until m) {
+ if (ints[j] == 0) {
+ count++
+ }
+ if (max < ints[j]) {
+ max = ints[j]
+ }
+ }
+ sum += max
+ }
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ var max = Int.MIN_VALUE
+ for (j in 0 until m) {
+ if (max < grid[j][i]) {
+ max = grid[j][i]
+ }
+ }
+ sum += max
+ }
+ return sum - count
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0884_uncommon_words_from_two_sentences/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0884_uncommon_words_from_two_sentences/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..698917c2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0884_uncommon_words_from_two_sentences/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 884\. Uncommon Words from Two Sentences
+
+Easy
+
+A **sentence** is a string of single-space separated words where each word consists only of lowercase letters.
+
+A word is **uncommon** if it appears exactly once in one of the sentences, and **does not appear** in the other sentence.
+
+Given two **sentences** `s1` and `s2`, return _a list of all the **uncommon words**_. You may return the answer in **any order**.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s1 = "this apple is sweet", s2 = "this apple is sour"
+
+**Output:** ["sweet","sour"]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s1 = "apple apple", s2 = "banana"
+
+**Output:** ["banana"]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= s1.length, s2.length <= 200`
+* `s1` and `s2` consist of lowercase English letters and spaces.
+* `s1` and `s2` do not have leading or trailing spaces.
+* All the words in `s1` and `s2` are separated by a single space.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun uncommonFromSentences(s1: String, s2: String): Array {
+ val visited = HashSet()
+ val uniques = HashSet()
+ for (word in s1.split(" ".toRegex()).dropLastWhile { it.isEmpty() }.toTypedArray()) {
+ if (!visited.add(word)) {
+ uniques.remove(word)
+ } else {
+ uniques.add(word)
+ }
+ }
+ for (word in s2.split(" ".toRegex()).dropLastWhile { it.isEmpty() }.toTypedArray()) {
+ if (!visited.add(word)) {
+ uniques.remove(word)
+ } else {
+ uniques.add(word)
+ }
+ }
+ val arr = arrayOfNulls(uniques.size)
+ for ((i, word) in uniques.withIndex()) {
+ arr[i] = word
+ }
+ return arr
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0885_spiral_matrix_iii/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0885_spiral_matrix_iii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9ecfd32f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0885_spiral_matrix_iii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,127 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 885\. Spiral Matrix III
+
+Medium
+
+You start at the cell `(rStart, cStart)` of an `rows x cols` grid facing east. The northwest corner is at the first row and column in the grid, and the southeast corner is at the last row and column.
+
+You will walk in a clockwise spiral shape to visit every position in this grid. Whenever you move outside the grid's boundary, we continue our walk outside the grid (but may return to the grid boundary later.). Eventually, we reach all `rows * cols` spaces of the grid.
+
+Return _an array of coordinates representing the positions of the grid in the order you visited them_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
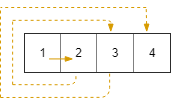
+**Input:** rows = 1, cols = 4, rStart = 0, cStart = 0
+
+**Output:** [[0,0],[0,1],[0,2],[0,3]]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
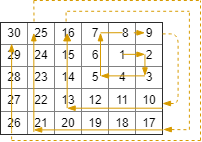
+**Input:** rows = 5, cols = 6, rStart = 1, cStart = 4
+
+**Output:** [[1,4],[1,5],[2,5],[2,4],[2,3],[1,3],[0,3],[0,4],[0,5],[3,5],[3,4],[3,3],[3,2],[2,2],[1,2],[0,2],[4,5],[4,4],[4,3],[4,2],[4,1],[3,1],[2,1],[1,1],[0,1],[4,0],[3,0],[2,0],[1,0],[0,0]]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= rows, cols <= 100`
+* `0 <= rStart < rows`
+* `0 <= cStart < cols`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+@Suppress("NAME_SHADOWING")
+class Solution {
+ fun spiralMatrixIII(rows: Int, cols: Int, y: Int, x: Int): Array {
+ var y = y
+ var x = x
+ var j: Int
+ var i = 0
+ var moves = 0
+ val result = Array(rows * cols) { IntArray(2) }
+ result[0][0] = y
+ result[0][1] = x
+ i++
+ while (i < result.size) {
+ moves++
+ // Move right
+ if (y < 0 || y >= rows) {
+ x += moves
+ } else {
+ j = 0
+ while (j < moves) {
+ x++
+ if (x in 0 until cols) {
+ result[i][0] = y
+ result[i][1] = x
+ i++
+ }
+ j++
+ }
+ }
+ if (i >= result.size) {
+ break
+ }
+ // Move down
+ if (x < 0 || x >= cols) {
+ y += moves
+ } else {
+ j = 0
+ while (j < moves) {
+ y++
+ if (y in 0 until rows) {
+ result[i][0] = y
+ result[i][1] = x
+ i++
+ }
+ j++
+ }
+ }
+ if (i >= result.size) {
+ break
+ }
+ moves++
+ // Move left
+ if (y < 0 || y >= rows) {
+ x -= moves
+ } else {
+ j = 0
+ while (j < moves) {
+ x--
+ if (x in 0 until cols) {
+ result[i][0] = y
+ result[i][1] = x
+ i++
+ }
+ j++
+ }
+ }
+ if (i >= result.size) {
+ break
+ }
+ // Move up
+ if (x < 0 || x >= cols) {
+ y -= moves
+ } else {
+ j = 0
+ while (j < moves) {
+ y--
+ if (y in 0 until rows) {
+ result[i][0] = y
+ result[i][1] = x
+ i++
+ }
+ j++
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return result
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0886_possible_bipartition/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0886_possible_bipartition/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e89bcce0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0886_possible_bipartition/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,93 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 886\. Possible Bipartition
+
+Medium
+
+We want to split a group of `n` people (labeled from `1` to `n`) into two groups of **any size**. Each person may dislike some other people, and they should not go into the same group.
+
+Given the integer `n` and the array `dislikes` where dislikes[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that the person labeled ai does not like the person labeled bi, return `true` _if it is possible to split everyone into two groups in this way_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 4, dislikes = \[\[1,2],[1,3],[2,4]]
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** The first group has [1,4], and the second group has [2,3].
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 3, dislikes = \[\[1,2],[1,3],[2,3]]
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Explanation:** We need at least 3 groups to divide them. We cannot put them in two groups.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= n <= 2000`
+* 0 <= dislikes.length <= 104
+* `dislikes[i].length == 2`
+* 1 <= ai < bi <= n
+* All the pairs of `dislikes` are **unique**.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun possibleBipartition(n: Int, dislikes: Array): Boolean {
+ // build graph
+ val g = Graph(n)
+ for (dislike in dislikes) {
+ g.addEdge(dislike[0] - 1, dislike[1] - 1)
+ }
+ val marked = BooleanArray(n)
+ val colors = BooleanArray(n)
+ for (v in 0 until n) {
+ if (!marked[v] && !checkBipartiteDFS(g, marked, colors, v)) {
+ // No need to run on other connected components if one component has failed.
+ return false
+ }
+ }
+ return true
+ }
+
+ private fun checkBipartiteDFS(g: Graph, marked: BooleanArray, colors: BooleanArray, v: Int): Boolean {
+ marked[v] = true
+ for (w in g.adj(v)) {
+ if (!marked[w]) {
+ colors[w] = !colors[v]
+ if (!checkBipartiteDFS(g, marked, colors, w)) {
+ // this is to break for other neighbours
+ return false
+ }
+ } else if (colors[v] == colors[w]) {
+ return false
+ }
+ }
+ return true
+ }
+
+ private class Graph(v: Int) {
+ private val adj: Array?>
+
+ init {
+ adj = arrayOfNulls(v)
+ for (i in 0 until v) {
+ adj[i] = ArrayList()
+ }
+ }
+
+ fun addEdge(v: Int, w: Int) {
+ adj[v]!!.add(w)
+ adj[w]!!.add(v)
+ }
+
+ fun adj(v: Int): List {
+ return adj[v]!!
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0887_super_egg_drop/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0887_super_egg_drop/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..dfc8f116
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0887_super_egg_drop/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 887\. Super Egg Drop
+
+Hard
+
+You are given `k` identical eggs and you have access to a building with `n` floors labeled from `1` to `n`.
+
+You know that there exists a floor `f` where `0 <= f <= n` such that any egg dropped at a floor **higher** than `f` will **break**, and any egg dropped **at or below** floor `f` will **not break**.
+
+Each move, you may take an unbroken egg and drop it from any floor `x` (where `1 <= x <= n`). If the egg breaks, you can no longer use it. However, if the egg does not break, you may **reuse** it in future moves.
+
+Return _the **minimum number of moves** that you need to determine **with certainty** what the value of_ `f` is.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** k = 1, n = 2
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Drop the egg from floor 1. If it breaks, we know that f = 0.
+
+Otherwise, drop the egg from floor 2. If it breaks, we know that f = 1.
+
+If it does not break, then we know f = 2.
+
+Hence, we need at minimum 2 moves to determine with certainty what the value of f is.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** k = 2, n = 6
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** k = 3, n = 14
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= k <= 100`
+* 1 <= n <= 104
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun superEggDrop(k: Int, n: Int): Int {
+ val dp = IntArray(k + 1)
+ var counter = 1
+ while (true) {
+ var temp = dp[0]
+ for (i in 1 until dp.size) {
+ val localValue = dp[i] + temp + 1
+ temp = dp[i]
+ dp[i] = localValue
+ if (localValue >= n) {
+ return counter
+ }
+ }
+ counter += 1
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0888_fair_candy_swap/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0888_fair_candy_swap/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..70db2676
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0888_fair_candy_swap/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 888\. Fair Candy Swap
+
+Easy
+
+Alice and Bob have a different total number of candies. You are given two integer arrays `aliceSizes` and `bobSizes` where `aliceSizes[i]` is the number of candies of the ith box of candy that Alice has and `bobSizes[j]` is the number of candies of the jth box of candy that Bob has.
+
+Since they are friends, they would like to exchange one candy box each so that after the exchange, they both have the same total amount of candy. The total amount of candy a person has is the sum of the number of candies in each box they have.
+
+Return a_n integer array_ `answer` _where_ `answer[0]` _is the number of candies in the box that Alice must exchange, and_ `answer[1]` _is the number of candies in the box that Bob must exchange_. If there are multiple answers, you may **return any** one of them. It is guaranteed that at least one answer exists.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** aliceSizes = [1,1], bobSizes = [2,2]
+
+**Output:** [1,2]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** aliceSizes = [1,2], bobSizes = [2,3]
+
+**Output:** [1,2]
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** aliceSizes = [2], bobSizes = [1,3]
+
+**Output:** [2,3]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= aliceSizes.length, bobSizes.length <= 104
+* 1 <= aliceSizes[i], bobSizes[j] <= 105
+* Alice and Bob have a different total number of candies.
+* There will be at least one valid answer for the given input.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun fairCandySwap(aliceSizes: IntArray, bobSizes: IntArray): IntArray {
+ var aSum = 0
+ var bSum = 0
+ val ans = IntArray(2)
+ for (bar in aliceSizes) {
+ aSum += bar
+ }
+ for (bar in bobSizes) {
+ bSum += bar
+ }
+ val diff: Int = aSum - bSum
+ val set: HashSet = HashSet()
+ for (bar in aliceSizes) {
+ set.add(bar)
+ }
+ for (bar in bobSizes) {
+ if (set.contains(bar + diff / 2)) {
+ ans[0] = bar + diff / 2
+ ans[1] = bar
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ return ans
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0889_construct_binary_tree_from_preorder_and_postorder_traversal/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0889_construct_binary_tree_from_preorder_and_postorder_traversal/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..51ff6e10
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0889_construct_binary_tree_from_preorder_and_postorder_traversal/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,100 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 889\. Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Postorder Traversal
+
+Medium
+
+Given two integer arrays, `preorder` and `postorder` where `preorder` is the preorder traversal of a binary tree of **distinct** values and `postorder` is the postorder traversal of the same tree, reconstruct and return _the binary tree_.
+
+If there exist multiple answers, you can **return any** of them.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** preorder = [1,2,4,5,3,6,7], postorder = [4,5,2,6,7,3,1]
+
+**Output:** [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** preorder = [1], postorder = [1]
+
+**Output:** [1]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= preorder.length <= 30`
+* `1 <= preorder[i] <= preorder.length`
+* All the values of `preorder` are **unique**.
+* `postorder.length == preorder.length`
+* `1 <= postorder[i] <= postorder.length`
+* All the values of `postorder` are **unique**.
+* It is guaranteed that `preorder` and `postorder` are the preorder traversal and postorder traversal of the same binary tree.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode
+
+/*
+ * Example:
+ * var ti = TreeNode(5)
+ * var v = ti.`val`
+ * Definition for a binary tree node.
+ * class TreeNode(var `val`: Int) {
+ * var left: TreeNode? = null
+ * var right: TreeNode? = null
+ * }
+ */
+class Solution {
+ fun constructFromPrePost(preorder: IntArray, postorder: IntArray): TreeNode? {
+ return if (preorder.isEmpty() || preorder.size != postorder.size) {
+ null
+ } else buildTree(preorder, 0, preorder.size - 1, postorder, 0, postorder.size - 1)
+ }
+
+ private fun buildTree(
+ preorder: IntArray,
+ preStart: Int,
+ preEnd: Int,
+ postorder: IntArray,
+ postStart: Int,
+ postEnd: Int
+ ): TreeNode? {
+ if (preStart > preEnd || postStart > postEnd) {
+ return null
+ }
+ val data = preorder[preStart]
+ val root = TreeNode(data)
+ if (preStart == preEnd) {
+ return root
+ }
+ var offset = postStart
+ while (offset <= preEnd) {
+ if (postorder[offset] == preorder[preStart + 1]) {
+ break
+ }
+ offset++
+ }
+ root.left = buildTree(
+ preorder,
+ preStart + 1,
+ preStart + offset - postStart + 1,
+ postorder,
+ postStart,
+ offset
+ )
+ root.right = buildTree(
+ preorder,
+ preStart + offset - postStart + 2,
+ preEnd,
+ postorder,
+ offset + 1,
+ postEnd - 1
+ )
+ return root
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0890_find_and_replace_pattern/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0890_find_and_replace_pattern/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f9d71af8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0890_find_and_replace_pattern/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 890\. Find and Replace Pattern
+
+Medium
+
+Given a list of strings `words` and a string `pattern`, return _a list of_ `words[i]` _that match_ `pattern`. You may return the answer in **any order**.
+
+A word matches the pattern if there exists a permutation of letters `p` so that after replacing every letter `x` in the pattern with `p(x)`, we get the desired word.
+
+Recall that a permutation of letters is a bijection from letters to letters: every letter maps to another letter, and no two letters map to the same letter.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** words = ["abc","deq","mee","aqq","dkd","ccc"], pattern = "abb"
+
+**Output:** ["mee","aqq"]
+
+**Explanation:** "mee" matches the pattern because there is a permutation {a -> m, b -> e, ...}. "ccc" does not match the pattern because {a -> c, b -> c, ...} is not a permutation, since a and b map to the same letter.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** words = ["a","b","c"], pattern = "a"
+
+**Output:** ["a","b","c"]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= pattern.length <= 20`
+* `1 <= words.length <= 50`
+* `words[i].length == pattern.length`
+* `pattern` and `words[i]` are lowercase English letters.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.Collections
+
+class Solution {
+ fun findAndReplacePattern(words: Array, pattern: String): List {
+ val finalans: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ if (pattern.length == 1) {
+ Collections.addAll(finalans, *words)
+ return finalans
+ }
+ for (word in words) {
+ val check = CharArray(26)
+ check.fill('1')
+ val ans: HashMap = HashMap()
+ for (j in word.indices) {
+ val pat = pattern[j]
+ val wor = word[j]
+ if (ans.containsKey(pat)) {
+ if (ans[pat] == wor) {
+ if (j == word.length - 1) {
+ finalans.add(word)
+ }
+ } else {
+ break
+ }
+ } else {
+ if (j == word.length - 1 && check[wor.code - 'a'.code] == '1') {
+ finalans.add(word)
+ }
+ if (check[wor.code - 'a'.code] != '1' && check[wor.code - 'a'.code] != pat) {
+ break
+ }
+ if (check[wor.code - 'a'.code] == '1') {
+ ans[pat] = wor
+ check[wor.code - 'a'.code] = pat
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return finalans
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0891_sum_of_subsequence_widths/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0891_sum_of_subsequence_widths/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..847130eb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0891_sum_of_subsequence_widths/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 891\. Sum of Subsequence Widths
+
+Hard
+
+The **width** of a sequence is the difference between the maximum and minimum elements in the sequence.
+
+Given an array of integers `nums`, return _the sum of the **widths** of all the non-empty **subsequences** of_ `nums`. Since the answer may be very large, return it **modulo** 109 + 7.
+
+A **subsequence** is a sequence that can be derived from an array by deleting some or no elements without changing the order of the remaining elements. For example, `[3,6,2,7]` is a subsequence of the array `[0,3,1,6,2,2,7]`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [2,1,3]
+
+**Output:** 6 Explanation: The subsequences are [1], [2], [3], [2,1], [2,3], [1,3], [2,1,3]. The corresponding widths are 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2. The sum of these widths is 6.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [2]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 105
+* 1 <= nums[i] <= 105
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ // 1-6 (number of elements in between 1 and 6) = (6-1-1) = 4
+ // length of sub seq 2 -> 4C0 3 -> 4C1 ; 4 -> 4c2 ; 5 -> 4C3 6 -> 4C4 4c0 + 4c1 + 4c2 + 4c3 +
+ // 4c4 1+4+6+4+1=16
+ // 1-5 3c0 + 3c1 + 3c2 + 3c3 = 8
+ // 1-4 2c0 + 2c1 2c2 = 4
+ // 1-3 1c0 + 1c1 = 2
+ // 1-2 1c0 = 1
+ /*
+ 16+8+4+2+1(for 1 as min) 8+4+2+1(for 2 as min) 4+2+1(for 3 as min) 2+1(for 4 as min) 1(for 5 as min)
+ -1*nums[0]*31 + nums[1]*1 + nums[2]*2 + nums[3]*4 + nums[4]*8 + nums[5]*16
+ -1*nums[1]*15 + nums[2]*1 +nums[3]*2 + nums[4]*4 + nums[5]*8
+ -1*nums[2]*7 + nums[3]*1 + nums[4]*2 + nums[5]*4
+ -1*nums[3]*3 + nums[4]*1 + nums[5]*2
+ -1*nums[4]*1 + nums[5]*1
+
+ -nums[0]*31 + -nums[1]*15 - nums[2]*7 - nums[3]*3 - nums[4]*1
+ nums[1]*1 + nums[2]*3 + nums[3]*7 + nums[4]*15 + nums[5]*31
+
+ (-1)*nums[0]*(pow[6-1-0]-1) + (-1)*nums[1]*(pow[6-1-1]-1) + (-1)*nums[2]*(pow[6-1-2]-1)
+ ... (-1)* nums[5]*(pow[6-1-5]-1)
+ + nums[1]*(pow[1]-1) + nums[2]*(pow[2]-1) + .... + nums[5]*(pow[5]-1)
+
+ (-1)*A[i]*(pow[l-1-i]-1) + A[i]*(pow[i]-1)
+ */
+ fun sumSubseqWidths(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ val mod = 1000000007
+ nums.sort()
+ val l = nums.size
+ val pow = LongArray(l)
+ pow[0] = 1
+ for (i in 1 until l) {
+ pow[i] = pow[i - 1] * 2 % mod
+ }
+ var res: Long = 0
+ for (i in 0 until l) {
+ res = (res + -1 * nums[i] * (pow[l - 1 - i] - 1) + nums[i] * (pow[i] - 1)) % mod
+ }
+ return res.toInt()
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file